President Yoweri Museveni’s mansion in Rwakitura is not just a village home—it is a massive, expensive, and heavily guarded residence that only a few Ugandans have ever seen up close. From the outside, the mansion looks like a luxury hotel, with cream-coloured walls, a red-tiled roof, wide balconies, and large tinted glass windows that stretch across the front.The house is built in a modern style and has multiple floors. It sits in the middle of a very large compound covered with green grass that is neatly cut. The entrance is wide and clean, with security guards stationed at every corner.Around the house are flower gardens and tall trees that give the place a calm and beautiful feeling. There are also well-paved walkways, water tanks, and large shaded parking areas.Museveni’s mansion is located deep in the countryside of Kiruhura District. The home is part of a big private farm where hundreds of cows move freely in the nearby fields. His cattle, mostly the long-horned Ankole breed, are kept in modern kraals, and there are milk stores and equipment nearby.
The house is not only a place for rest but is also used for state meetings, where he hosts visitors including government officials and foreign guests.Inside the mansion, although cameras are not allowed, some sources say the interior has shiny tiled floors, large leather chairs, big TVs, soft carpets, and spacious rooms. The sitting room is believed to be very large, with decorated ceilings and art pieces on the walls. Every section of the house looks carefully planned and furnished to high standards.
Blog
-
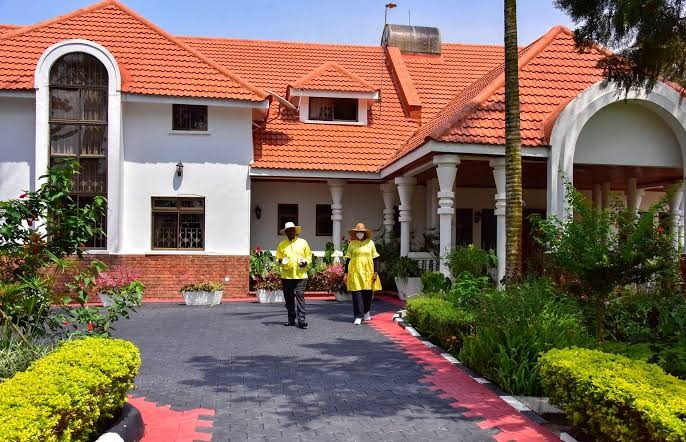

Take a Look Inside Museveni’s Multi-Billion Mansion That Few Ugandans Have Ever Seen (Photos)
-
How thinking about ‘future you’ can build a happier life
Space scientists have discovered just how much they can accomplish when they work together, with incredible feats achieved this year through collaborations with commercial industry and foreign nations.
Successful partnerships in 2022 have included the launch and calibration of the most powerful space telescope in the world and photographing the never-before-seen supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
Space, it says, is big. Really big. You just won’t believe how vastly, hugely, mindbogglingly big it is.
Douglas AdamsStray rocket junk in an unpredictable orbit smashed into the moon, for example, creating a new crater. And NASA’s mega moon rocket, the Space Launch System, has stumbled on its way to its first lunar mission, with the agency encountering several problems with contractors’ work during a critical test this spring.
Whether the rest of the year will include the inaugural moon-bound Artemis mission, the United States’ return to human deep space exploration, remains to be seen. Read more about the year’s biggest moments in space, so far.
James Webb Space Telescope opens for business
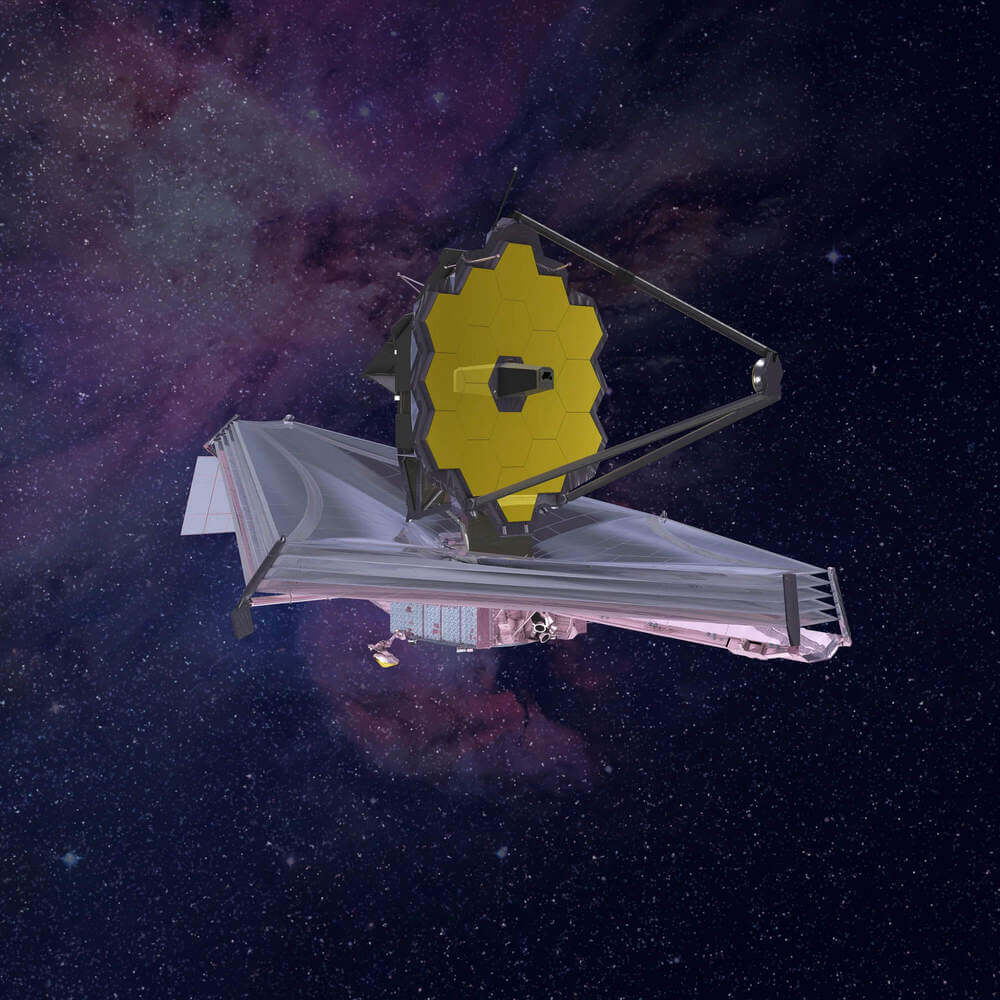

The James Webb Space Telescope will deliver its first full-color images on July 12. Credit: NASA The most powerful observatory in space hit its mark at a destination 1 million miles from Earth in late January and unfurled its complicated, tennis court-size sun shield. Engineers have since calibrated the Webb telescope’s scientific instruments, exceeding expectations for its level of precision.
In this single galaxy of ours there are eighty-seven thousand million suns.
Arthur C. ClarkeAstronomers anticipate the telescope will stoke a golden age in our understanding of the cosmos, providing snapshots of space billions of light-years away.
On July 12, the James Webb Space Telescope, a partnership between NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency, will deliver its first full-color images. What those first cosmic targets will be is a closely guarded secret.
Webb is expected to observe some of the oldest, faintest light in the universe. The telescope will focus on a period less than 300 million years after the Big Bang, when many of the first stars and galaxies were born.
Scientists will also use the telescope to peer into the atmospheres of planets outside our solar system, called exoplanets. Discoveries out there of water and methane, for example, could be signs of potential habitability or biological activity.
Peculiar widespread Martian aurora discovered
New overview images of Mars have revealed a stunning green light show in the planet’s sky.
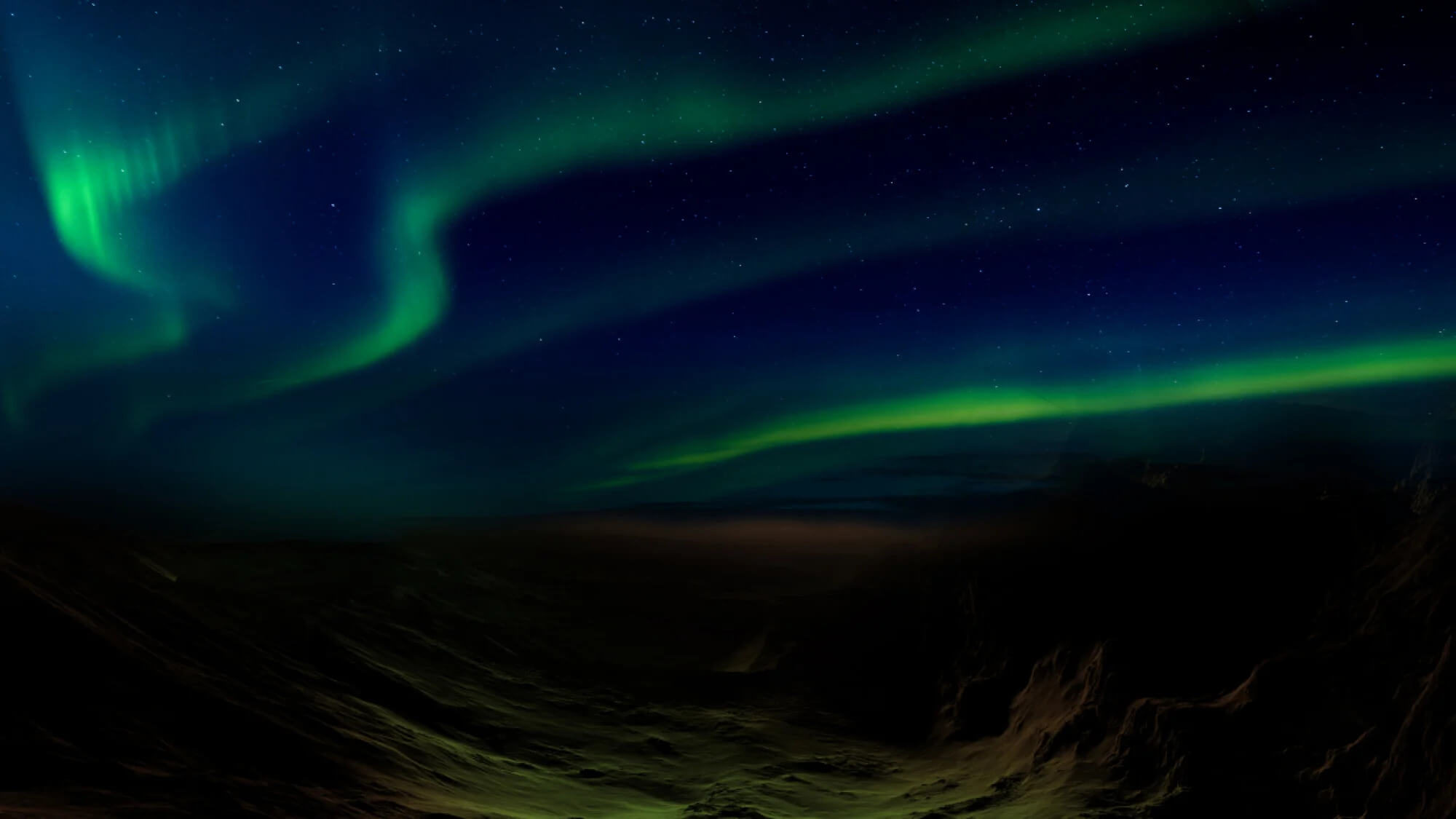

Scientists believe a newly discovered Martian aurora puts green streaks in Mars’ sky. Credit: Emirates Mars Mission Much of Mars’ atmosphere apparently has a wormlike streak, an aurora similar to the Northern Lights sometimes visible on Earth. The Martian aurora is a glowing, twisted band of ultraviolet light, stretching thousands of miles from the dayside, which faces the sun, to the back of the planet.
A United Arab Emirates Space Agency probe orbiting Mars, known as Hope, took the snapshots.
No one knows how it’s happening, given that scientists believe Mars’ magnetic field largely deteriorated billions of years ago. Magnetic fields guide high-energy streams of electrons from the sun into a planet’s atmosphere.
Astronomers take the first photo of massive Milky Way black hole
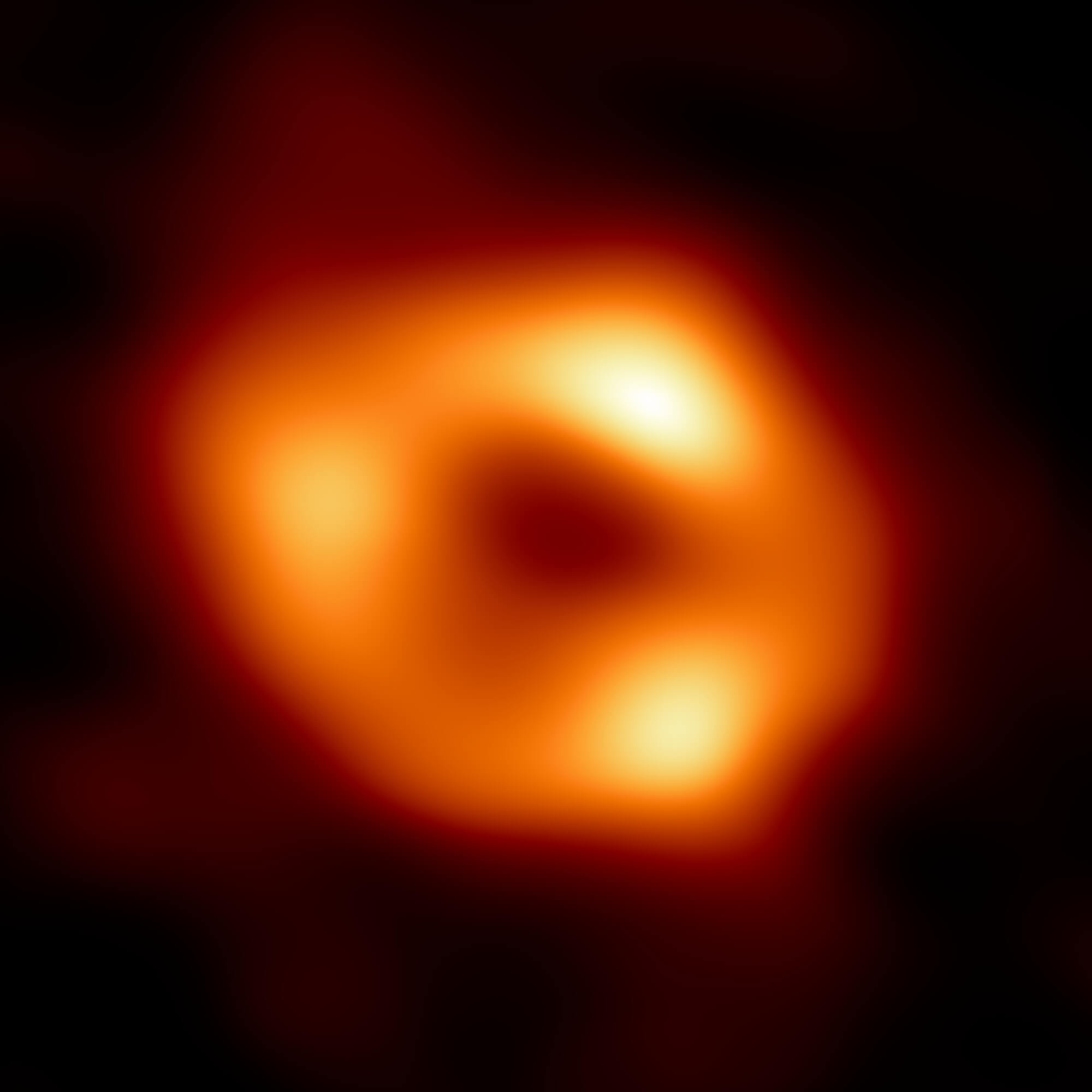

Scientists around the world worked together to take the first photo ever of Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Credit: Event Horizon Telescope At the center of the Milky Way is a giant black hole, and for the first time ever, astronomers were able to see it.
Black holes don’t have surfaces, like planets or stars. Instead, these mysterious cosmic objects have a boundary called an “event horizon,” a point of no return. If anything swoops too close to that point, it will fall inward, never to escape the hole’s gravity.
With the power of eight linked radio dishes from around the world, the Event Horizon Telescope took a picture of the shadow of the supermassive black hole known as Sagittarius A*. Hundreds of scientists from 80 institutions around the globe worked together to collect, process, and piece together fragments of data to make the picture.
Up until three years ago, any depiction of a black hole was merely an artist’s interpretation or a computer model. Now scientists have a snapshot of the real deal, which spans 27 million miles.
With financial support from the National Science Foundation and other groups, scientists plan to enhance their technology to make the image drastically sharper.
-
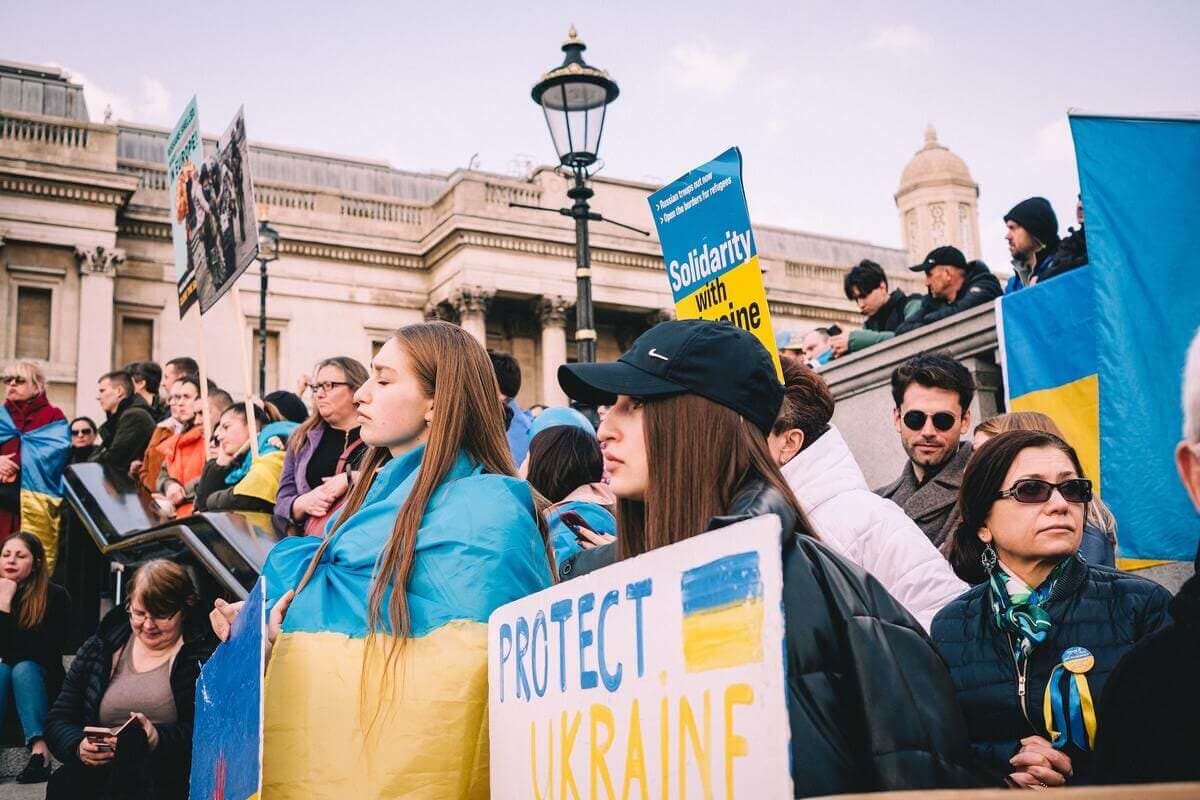

The war in Ukraine: Meet the people resisting the Russian invasion
Space scientists have discovered just how much they can accomplish when they work together, with incredible feats achieved this year through collaborations with commercial industry and foreign nations.
Successful partnerships in 2022 have included the launch and calibration of the most powerful space telescope in the world and photographing the never-before-seen supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
Space, it says, is big. Really big. You just won’t believe how vastly, hugely, mindbogglingly big it is.
Douglas AdamsStray rocket junk in an unpredictable orbit smashed into the moon, for example, creating a new crater. And NASA’s mega moon rocket, the Space Launch System, has stumbled on its way to its first lunar mission, with the agency encountering several problems with contractors’ work during a critical test this spring.
Whether the rest of the year will include the inaugural moon-bound Artemis mission, the United States’ return to human deep space exploration, remains to be seen. Read more about the year’s biggest moments in space, so far.
James Webb Space Telescope opens for business

The James Webb Space Telescope will deliver its first full-color images on July 12. Credit: NASA The most powerful observatory in space hit its mark at a destination 1 million miles from Earth in late January and unfurled its complicated, tennis court-size sun shield. Engineers have since calibrated the Webb telescope’s scientific instruments, exceeding expectations for its level of precision.
In this single galaxy of ours there are eighty-seven thousand million suns.
Arthur C. ClarkeAstronomers anticipate the telescope will stoke a golden age in our understanding of the cosmos, providing snapshots of space billions of light-years away.
On July 12, the James Webb Space Telescope, a partnership between NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency, will deliver its first full-color images. What those first cosmic targets will be is a closely guarded secret.
Webb is expected to observe some of the oldest, faintest light in the universe. The telescope will focus on a period less than 300 million years after the Big Bang, when many of the first stars and galaxies were born.
Scientists will also use the telescope to peer into the atmospheres of planets outside our solar system, called exoplanets. Discoveries out there of water and methane, for example, could be signs of potential habitability or biological activity.
Peculiar widespread Martian aurora discovered
New overview images of Mars have revealed a stunning green light show in the planet’s sky.

Scientists believe a newly discovered Martian aurora puts green streaks in Mars’ sky. Credit: Emirates Mars Mission Much of Mars’ atmosphere apparently has a wormlike streak, an aurora similar to the Northern Lights sometimes visible on Earth. The Martian aurora is a glowing, twisted band of ultraviolet light, stretching thousands of miles from the dayside, which faces the sun, to the back of the planet.
A United Arab Emirates Space Agency probe orbiting Mars, known as Hope, took the snapshots.
No one knows how it’s happening, given that scientists believe Mars’ magnetic field largely deteriorated billions of years ago. Magnetic fields guide high-energy streams of electrons from the sun into a planet’s atmosphere.
Astronomers take the first photo of massive Milky Way black hole

Scientists around the world worked together to take the first photo ever of Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Credit: Event Horizon Telescope At the center of the Milky Way is a giant black hole, and for the first time ever, astronomers were able to see it.
Black holes don’t have surfaces, like planets or stars. Instead, these mysterious cosmic objects have a boundary called an “event horizon,” a point of no return. If anything swoops too close to that point, it will fall inward, never to escape the hole’s gravity.
With the power of eight linked radio dishes from around the world, the Event Horizon Telescope took a picture of the shadow of the supermassive black hole known as Sagittarius A*. Hundreds of scientists from 80 institutions around the globe worked together to collect, process, and piece together fragments of data to make the picture.
Up until three years ago, any depiction of a black hole was merely an artist’s interpretation or a computer model. Now scientists have a snapshot of the real deal, which spans 27 million miles.
With financial support from the National Science Foundation and other groups, scientists plan to enhance their technology to make the image drastically sharper.
-

Perfect Zodiac Gifts For Astrology Lovers That Any Sign Will Appreciate
Space scientists have discovered just how much they can accomplish when they work together, with incredible feats achieved this year through collaborations with commercial industry and foreign nations.
Successful partnerships in 2022 have included the launch and calibration of the most powerful space telescope in the world and photographing the never-before-seen supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
(more…) -

Binance’s BNB cryptocurrency hit by massive $100 million hack
Space scientists have discovered just how much they can accomplish when they work together, with incredible feats achieved this year through collaborations with commercial industry and foreign nations.
Successful partnerships in 2022 have included the launch and calibration of the most powerful space telescope in the world and photographing the never-before-seen supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
Space, it says, is big. Really big. You just won’t believe how vastly, hugely, mindbogglingly big it is.
Douglas AdamsStray rocket junk in an unpredictable orbit smashed into the moon, for example, creating a new crater. And NASA’s mega moon rocket, the Space Launch System, has stumbled on its way to its first lunar mission, with the agency encountering several problems with contractors’ work during a critical test this spring.
Whether the rest of the year will include the inaugural moon-bound Artemis mission, the United States’ return to human deep space exploration, remains to be seen. Read more about the year’s biggest moments in space, so far.
James Webb Space Telescope opens for business

The James Webb Space Telescope will deliver its first full-color images on July 12. Credit: NASA The most powerful observatory in space hit its mark at a destination 1 million miles from Earth in late January and unfurled its complicated, tennis court-size sun shield. Engineers have since calibrated the Webb telescope’s scientific instruments, exceeding expectations for its level of precision.
In this single galaxy of ours there are eighty-seven thousand million suns.
Arthur C. ClarkeAstronomers anticipate the telescope will stoke a golden age in our understanding of the cosmos, providing snapshots of space billions of light-years away.
On July 12, the James Webb Space Telescope, a partnership between NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency, will deliver its first full-color images. What those first cosmic targets will be is a closely guarded secret.
Webb is expected to observe some of the oldest, faintest light in the universe. The telescope will focus on a period less than 300 million years after the Big Bang, when many of the first stars and galaxies were born.
Scientists will also use the telescope to peer into the atmospheres of planets outside our solar system, called exoplanets. Discoveries out there of water and methane, for example, could be signs of potential habitability or biological activity.
Peculiar widespread Martian aurora discovered
New overview images of Mars have revealed a stunning green light show in the planet’s sky.

Scientists believe a newly discovered Martian aurora puts green streaks in Mars’ sky. Credit: Emirates Mars Mission Much of Mars’ atmosphere apparently has a wormlike streak, an aurora similar to the Northern Lights sometimes visible on Earth. The Martian aurora is a glowing, twisted band of ultraviolet light, stretching thousands of miles from the dayside, which faces the sun, to the back of the planet.
A United Arab Emirates Space Agency probe orbiting Mars, known as Hope, took the snapshots.
No one knows how it’s happening, given that scientists believe Mars’ magnetic field largely deteriorated billions of years ago. Magnetic fields guide high-energy streams of electrons from the sun into a planet’s atmosphere.
Astronomers take the first photo of massive Milky Way black hole

Scientists around the world worked together to take the first photo ever of Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Credit: Event Horizon Telescope At the center of the Milky Way is a giant black hole, and for the first time ever, astronomers were able to see it.
Black holes don’t have surfaces, like planets or stars. Instead, these mysterious cosmic objects have a boundary called an “event horizon,” a point of no return. If anything swoops too close to that point, it will fall inward, never to escape the hole’s gravity.
With the power of eight linked radio dishes from around the world, the Event Horizon Telescope took a picture of the shadow of the supermassive black hole known as Sagittarius A*. Hundreds of scientists from 80 institutions around the globe worked together to collect, process, and piece together fragments of data to make the picture.
Up until three years ago, any depiction of a black hole was merely an artist’s interpretation or a computer model. Now scientists have a snapshot of the real deal, which spans 27 million miles.
With financial support from the National Science Foundation and other groups, scientists plan to enhance their technology to make the image drastically sharper.
-

Robot companies pledge they’re not going to let the robots kill you
Space scientists have discovered just how much they can accomplish when they work together, with incredible feats achieved this year through collaborations with commercial industry and foreign nations.
Successful partnerships in 2022 have included the launch and calibration of the most powerful space telescope in the world and photographing the never-before-seen supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
Space, it says, is big. Really big. You just won’t believe how vastly, hugely, mindbogglingly big it is.
Douglas AdamsStray rocket junk in an unpredictable orbit smashed into the moon, for example, creating a new crater. And NASA’s mega moon rocket, the Space Launch System, has stumbled on its way to its first lunar mission, with the agency encountering several problems with contractors’ work during a critical test this spring.
Whether the rest of the year will include the inaugural moon-bound Artemis mission, the United States’ return to human deep space exploration, remains to be seen. Read more about the year’s biggest moments in space, so far.
James Webb Space Telescope opens for business

The James Webb Space Telescope will deliver its first full-color images on July 12. Credit: NASA The most powerful observatory in space hit its mark at a destination 1 million miles from Earth in late January and unfurled its complicated, tennis court-size sun shield. Engineers have since calibrated the Webb telescope’s scientific instruments, exceeding expectations for its level of precision.
In this single galaxy of ours there are eighty-seven thousand million suns.
Arthur C. ClarkeAstronomers anticipate the telescope will stoke a golden age in our understanding of the cosmos, providing snapshots of space billions of light-years away.
On July 12, the James Webb Space Telescope, a partnership between NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency, will deliver its first full-color images. What those first cosmic targets will be is a closely guarded secret.
Webb is expected to observe some of the oldest, faintest light in the universe. The telescope will focus on a period less than 300 million years after the Big Bang, when many of the first stars and galaxies were born.
Scientists will also use the telescope to peer into the atmospheres of planets outside our solar system, called exoplanets. Discoveries out there of water and methane, for example, could be signs of potential habitability or biological activity.
Peculiar widespread Martian aurora discovered
New overview images of Mars have revealed a stunning green light show in the planet’s sky.

Scientists believe a newly discovered Martian aurora puts green streaks in Mars’ sky. Credit: Emirates Mars Mission Much of Mars’ atmosphere apparently has a wormlike streak, an aurora similar to the Northern Lights sometimes visible on Earth. The Martian aurora is a glowing, twisted band of ultraviolet light, stretching thousands of miles from the dayside, which faces the sun, to the back of the planet.
A United Arab Emirates Space Agency probe orbiting Mars, known as Hope, took the snapshots.
No one knows how it’s happening, given that scientists believe Mars’ magnetic field largely deteriorated billions of years ago. Magnetic fields guide high-energy streams of electrons from the sun into a planet’s atmosphere.
Astronomers take the first photo of massive Milky Way black hole

Scientists around the world worked together to take the first photo ever of Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Credit: Event Horizon Telescope At the center of the Milky Way is a giant black hole, and for the first time ever, astronomers were able to see it.
Black holes don’t have surfaces, like planets or stars. Instead, these mysterious cosmic objects have a boundary called an “event horizon,” a point of no return. If anything swoops too close to that point, it will fall inward, never to escape the hole’s gravity.
With the power of eight linked radio dishes from around the world, the Event Horizon Telescope took a picture of the shadow of the supermassive black hole known as Sagittarius A*. Hundreds of scientists from 80 institutions around the globe worked together to collect, process, and piece together fragments of data to make the picture.
Up until three years ago, any depiction of a black hole was merely an artist’s interpretation or a computer model. Now scientists have a snapshot of the real deal, which spans 27 million miles.
With financial support from the National Science Foundation and other groups, scientists plan to enhance their technology to make the image drastically sharper.
-

Everything you need to know about Amazon’s Prime Early Access Sale next week
Space scientists have discovered just how much they can accomplish when they work together, with incredible feats achieved this year through collaborations with commercial industry and foreign nations.
Successful partnerships in 2022 have included the launch and calibration of the most powerful space telescope in the world and photographing the never-before-seen supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
(more…) -

Do We Really Need To Wear Hair Products That Contain Sunscreen?
Space scientists have discovered just how much they can accomplish when they work together, with incredible feats achieved this year through collaborations with commercial industry and foreign nations.
Successful partnerships in 2022 have included the launch and calibration of the most powerful space telescope in the world and photographing the never-before-seen supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
Space, it says, is big. Really big. You just won’t believe how vastly, hugely, mindbogglingly big it is.
Douglas AdamsStray rocket junk in an unpredictable orbit smashed into the moon, for example, creating a new crater. And NASA’s mega moon rocket, the Space Launch System, has stumbled on its way to its first lunar mission, with the agency encountering several problems with contractors’ work during a critical test this spring.
Whether the rest of the year will include the inaugural moon-bound Artemis mission, the United States’ return to human deep space exploration, remains to be seen. Read more about the year’s biggest moments in space, so far.
James Webb Space Telescope opens for business

The James Webb Space Telescope will deliver its first full-color images on July 12. Credit: NASA The most powerful observatory in space hit its mark at a destination 1 million miles from Earth in late January and unfurled its complicated, tennis court-size sun shield. Engineers have since calibrated the Webb telescope’s scientific instruments, exceeding expectations for its level of precision.
In this single galaxy of ours there are eighty-seven thousand million suns.
Arthur C. ClarkeAstronomers anticipate the telescope will stoke a golden age in our understanding of the cosmos, providing snapshots of space billions of light-years away.
On July 12, the James Webb Space Telescope, a partnership between NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency, will deliver its first full-color images. What those first cosmic targets will be is a closely guarded secret.
Webb is expected to observe some of the oldest, faintest light in the universe. The telescope will focus on a period less than 300 million years after the Big Bang, when many of the first stars and galaxies were born.
Scientists will also use the telescope to peer into the atmospheres of planets outside our solar system, called exoplanets. Discoveries out there of water and methane, for example, could be signs of potential habitability or biological activity.
Peculiar widespread Martian aurora discovered
New overview images of Mars have revealed a stunning green light show in the planet’s sky.

Scientists believe a newly discovered Martian aurora puts green streaks in Mars’ sky. Credit: Emirates Mars Mission Much of Mars’ atmosphere apparently has a wormlike streak, an aurora similar to the Northern Lights sometimes visible on Earth. The Martian aurora is a glowing, twisted band of ultraviolet light, stretching thousands of miles from the dayside, which faces the sun, to the back of the planet.
A United Arab Emirates Space Agency probe orbiting Mars, known as Hope, took the snapshots.
No one knows how it’s happening, given that scientists believe Mars’ magnetic field largely deteriorated billions of years ago. Magnetic fields guide high-energy streams of electrons from the sun into a planet’s atmosphere.
Astronomers take the first photo of massive Milky Way black hole

Scientists around the world worked together to take the first photo ever of Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Credit: Event Horizon Telescope At the center of the Milky Way is a giant black hole, and for the first time ever, astronomers were able to see it.
Black holes don’t have surfaces, like planets or stars. Instead, these mysterious cosmic objects have a boundary called an “event horizon,” a point of no return. If anything swoops too close to that point, it will fall inward, never to escape the hole’s gravity.
With the power of eight linked radio dishes from around the world, the Event Horizon Telescope took a picture of the shadow of the supermassive black hole known as Sagittarius A*. Hundreds of scientists from 80 institutions around the globe worked together to collect, process, and piece together fragments of data to make the picture.
Up until three years ago, any depiction of a black hole was merely an artist’s interpretation or a computer model. Now scientists have a snapshot of the real deal, which spans 27 million miles.
With financial support from the National Science Foundation and other groups, scientists plan to enhance their technology to make the image drastically sharper.
-

The One Side Effect Of Trauma We Rarely Talk About
Space scientists have discovered just how much they can accomplish when they work together, with incredible feats achieved this year through collaborations with commercial industry and foreign nations.
Successful partnerships in 2022 have included the launch and calibration of the most powerful space telescope in the world and photographing the never-before-seen supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
Space, it says, is big. Really big. You just won’t believe how vastly, hugely, mindbogglingly big it is.
Douglas AdamsStray rocket junk in an unpredictable orbit smashed into the moon, for example, creating a new crater. And NASA’s mega moon rocket, the Space Launch System, has stumbled on its way to its first lunar mission, with the agency encountering several problems with contractors’ work during a critical test this spring.
Whether the rest of the year will include the inaugural moon-bound Artemis mission, the United States’ return to human deep space exploration, remains to be seen. Read more about the year’s biggest moments in space, so far.
James Webb Space Telescope opens for business

The James Webb Space Telescope will deliver its first full-color images on July 12. Credit: NASA The most powerful observatory in space hit its mark at a destination 1 million miles from Earth in late January and unfurled its complicated, tennis court-size sun shield. Engineers have since calibrated the Webb telescope’s scientific instruments, exceeding expectations for its level of precision.
In this single galaxy of ours there are eighty-seven thousand million suns.
Arthur C. ClarkeAstronomers anticipate the telescope will stoke a golden age in our understanding of the cosmos, providing snapshots of space billions of light-years away.
On July 12, the James Webb Space Telescope, a partnership between NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency, will deliver its first full-color images. What those first cosmic targets will be is a closely guarded secret.
Webb is expected to observe some of the oldest, faintest light in the universe. The telescope will focus on a period less than 300 million years after the Big Bang, when many of the first stars and galaxies were born.
Scientists will also use the telescope to peer into the atmospheres of planets outside our solar system, called exoplanets. Discoveries out there of water and methane, for example, could be signs of potential habitability or biological activity.
Peculiar widespread Martian aurora discovered
New overview images of Mars have revealed a stunning green light show in the planet’s sky.

Scientists believe a newly discovered Martian aurora puts green streaks in Mars’ sky. Credit: Emirates Mars Mission Much of Mars’ atmosphere apparently has a wormlike streak, an aurora similar to the Northern Lights sometimes visible on Earth. The Martian aurora is a glowing, twisted band of ultraviolet light, stretching thousands of miles from the dayside, which faces the sun, to the back of the planet.
A United Arab Emirates Space Agency probe orbiting Mars, known as Hope, took the snapshots.
No one knows how it’s happening, given that scientists believe Mars’ magnetic field largely deteriorated billions of years ago. Magnetic fields guide high-energy streams of electrons from the sun into a planet’s atmosphere.
Astronomers take the first photo of massive Milky Way black hole

Scientists around the world worked together to take the first photo ever of Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Credit: Event Horizon Telescope At the center of the Milky Way is a giant black hole, and for the first time ever, astronomers were able to see it.
Black holes don’t have surfaces, like planets or stars. Instead, these mysterious cosmic objects have a boundary called an “event horizon,” a point of no return. If anything swoops too close to that point, it will fall inward, never to escape the hole’s gravity.
With the power of eight linked radio dishes from around the world, the Event Horizon Telescope took a picture of the shadow of the supermassive black hole known as Sagittarius A*. Hundreds of scientists from 80 institutions around the globe worked together to collect, process, and piece together fragments of data to make the picture.
Up until three years ago, any depiction of a black hole was merely an artist’s interpretation or a computer model. Now scientists have a snapshot of the real deal, which spans 27 million miles.
With financial support from the National Science Foundation and other groups, scientists plan to enhance their technology to make the image drastically sharper.
-

Here’s What An Astrologer Wants You To Know About Horoscopes
Space scientists have discovered just how much they can accomplish when they work together, with incredible feats achieved this year through collaborations with commercial industry and foreign nations.
Successful partnerships in 2022 have included the launch and calibration of the most powerful space telescope in the world and photographing the never-before-seen supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
Space, it says, is big. Really big. You just won’t believe how vastly, hugely, mindbogglingly big it is.
Douglas AdamsStray rocket junk in an unpredictable orbit smashed into the moon, for example, creating a new crater. And NASA’s mega moon rocket, the Space Launch System, has stumbled on its way to its first lunar mission, with the agency encountering several problems with contractors’ work during a critical test this spring.
Whether the rest of the year will include the inaugural moon-bound Artemis mission, the United States’ return to human deep space exploration, remains to be seen. Read more about the year’s biggest moments in space, so far.
James Webb Space Telescope opens for business

The James Webb Space Telescope will deliver its first full-color images on July 12. Credit: NASA The most powerful observatory in space hit its mark at a destination 1 million miles from Earth in late January and unfurled its complicated, tennis court-size sun shield. Engineers have since calibrated the Webb telescope’s scientific instruments, exceeding expectations for its level of precision.
In this single galaxy of ours there are eighty-seven thousand million suns.
Arthur C. ClarkeAstronomers anticipate the telescope will stoke a golden age in our understanding of the cosmos, providing snapshots of space billions of light-years away.
On July 12, the James Webb Space Telescope, a partnership between NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency, will deliver its first full-color images. What those first cosmic targets will be is a closely guarded secret.
Webb is expected to observe some of the oldest, faintest light in the universe. The telescope will focus on a period less than 300 million years after the Big Bang, when many of the first stars and galaxies were born.
Scientists will also use the telescope to peer into the atmospheres of planets outside our solar system, called exoplanets. Discoveries out there of water and methane, for example, could be signs of potential habitability or biological activity.
Peculiar widespread Martian aurora discovered
New overview images of Mars have revealed a stunning green light show in the planet’s sky.

Scientists believe a newly discovered Martian aurora puts green streaks in Mars’ sky. Credit: Emirates Mars Mission Much of Mars’ atmosphere apparently has a wormlike streak, an aurora similar to the Northern Lights sometimes visible on Earth. The Martian aurora is a glowing, twisted band of ultraviolet light, stretching thousands of miles from the dayside, which faces the sun, to the back of the planet.
A United Arab Emirates Space Agency probe orbiting Mars, known as Hope, took the snapshots.
No one knows how it’s happening, given that scientists believe Mars’ magnetic field largely deteriorated billions of years ago. Magnetic fields guide high-energy streams of electrons from the sun into a planet’s atmosphere.
Astronomers take the first photo of massive Milky Way black hole

Scientists around the world worked together to take the first photo ever of Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Credit: Event Horizon Telescope At the center of the Milky Way is a giant black hole, and for the first time ever, astronomers were able to see it.
Black holes don’t have surfaces, like planets or stars. Instead, these mysterious cosmic objects have a boundary called an “event horizon,” a point of no return. If anything swoops too close to that point, it will fall inward, never to escape the hole’s gravity.
With the power of eight linked radio dishes from around the world, the Event Horizon Telescope took a picture of the shadow of the supermassive black hole known as Sagittarius A*. Hundreds of scientists from 80 institutions around the globe worked together to collect, process, and piece together fragments of data to make the picture.
Up until three years ago, any depiction of a black hole was merely an artist’s interpretation or a computer model. Now scientists have a snapshot of the real deal, which spans 27 million miles.
With financial support from the National Science Foundation and other groups, scientists plan to enhance their technology to make the image drastically sharper.